Porcelain tiles and ceramics are the two most popular choices as wall and floor coverings for both residential and commercial projects. However, despite being so popular, barely people know the actual difference between porcelain and ceramic tiles.
However, identifying porcelain tiles and ceramic tiles is important to make crucial decisions for transforming spaces. They are different in composition, water absorption, and many more aspects. Thus, the selection can affect the space's durability and project budget.
So, how to distinguish between these two materials? Don't worry, we have brought you a comprehensive tiles comparison guide to help you make a wise decision.
Ceramic Vs. Porcelain Tiles: A Comprehensive Guide
1. Water Absorption

One important factor in differentiating porcelain from ceramic tiles is water absorption. With a water absorption rate of less than 0.5%, porcelain tiles are particularly impermeable, making them ideal for bathrooms, outdoor spaces, and settings with high moisture content.
Ceramic tiles are more suitable for interior use in low-moisture environments, such as kitchens or living rooms, because of their higher absorption rates. The production process determines this characteristic; porcelain is burned at higher temperatures than ceramic, generating a denser and far less porous surface. Their differences in absorption may be found with a simple test using water.
2. PEI Rating

The Porcelain Enamel Institute (PEI) Rating is a reliable measure of a tile's durability and resistance to wear. Porcelain tiles often have a PEI rating of 4 or 5, making them highly suitable for heavy foot traffic areas such as commercial spaces or outdoor pathways.
Ceramic tiles generally have a PEI rating of 1 to 3, making them better for light-use areas like walls or low-traffic rooms. Understanding the PEI rating ensures the right tile is selected for the intended purpose, balancing longevity and functionality. Always check the PEI rating label when evaluating tiles for specific applications.
3. Tile Edges

Tile edges provide visual and functional clues to differentiate porcelain from ceramic. Porcelain tiles often feature rectified edges, which are precisely cut for uniformity, allowing tight grout lines and a seamless finish. This makes them popular for modern or minimalist designs.
Ceramic tiles typically have softer, rounded edges, resulting in wider grout lines and a more casual, traditional look. The difference in edge finish is due to porcelain's harder composition, which enables precise cutting. By examining the edges of a tile, you can identify its material type and choose the style that best matches your design preferences.
4. Tile Thickness

Tile thickness is another indicative sign to identify porcelain and ceramic. Porcelain tiles are typically thicker and denser, making them more durable and resistant to wear. Their extra thickness ensures long-lasting performance in high-traffic or heavy-use areas, such as commercial floors or outdoor patios.
Whereas, Ceramic tiles are thinner and lighter, which makes them easier to install but less robust in demanding environments. While thinner tiles may suffice for wall applications or light-use floors, porcelain’s additional thickness provides strength and durability for more rigorous conditions, ensuring better performance and value in the long run.
5. Scratch Test

A simple scratch test can reveal whether a tile is porcelain or ceramic. Porcelain’s harder surface is more resistant to scratches, making it ideal for areas prone to heavy use, such as kitchens, hallways, or outdoor patios. Ceramic tiles, being softer, are more likely to show marks or scratches when subjected to sharp objects.
This difference in scratch resistance is due to the denser composition of porcelain, fired at higher temperatures. Performing a light scratch test on an inconspicuous area or sample piece can help determine the material’s durability and whether it meets the specific needs of your space.
6. Density

Density plays a significant role in distinguishing porcelain from ceramic. Porcelain tiles are denser and heavier because they are made from finer clay and fired at higher temperatures. This results in a harder and more durable material that can withstand high traffic and adverse weather conditions.
On the other hand, Ceramic tiles are less dense and lighter, making them easier to handle and install but less durable in demanding environments. Density also impacts the tile's feel; porcelain often feels cooler and smoother compared to ceramic. If you need a long-lasting tile, especially for outdoor use, porcelain is the superior choice.
7. Price

Price is a key factor when choosing between porcelain and ceramic tiles. Ceramic tiles are generally more affordable, making them a budget-friendly option for homeowners seeking aesthetic appeal without breaking the bank. Porcelain tiles, on the other hand, are more expensive due to their enhanced durability, lower water absorption, and versatile applications.
While porcelain’s premium price may seem steep, its long-term benefits in high-traffic or moisture-prone areas justify the investment. For areas like walls or low-use rooms, ceramic tiles offer a cost-effective solution. Balancing budget and performance is essential to choosing the right tile for your project.
8. Color Through the Tile
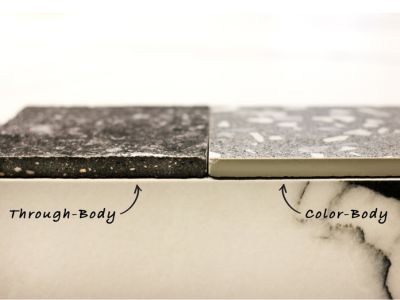
Some porcelain tile types like full-body tiles are often made with a through-body composition, meaning the colour and pattern extend through the entire tile. This ensures that chips or scratches are less visible, making them ideal for high-traffic areas.
Ceramic tiles, however, typically have a glazed top layer with a different base colour, so chips or wear reveal the underlying material, affecting aesthetics. By examining the back or side of the tile, you can observe whether the colour and texture are consistent, helping to differentiate between the two materials and select the one that fits your durability and design needs.
9. Glazing and Finish

Porcelain and ceramic tiles differ in their glazing options. Porcelain can be either glazed or unglazed, with unglazed porcelain often preferred for outdoor areas due to its slip resistance.
On the other hand, the majority of ceramic tiles available in the market are indeed glazed, providing vibrant colours and a glossy finish.
The glaze on ceramic tiles also adds a protective layer but is less durable than the surface of unglazed porcelain. Scratching or tapping the tile surface can reveal whether the tile has a glazed or natural finish, helping determine whether it is porcelain or ceramic and its suitability for specific areas.
10. Heat Resistance

Porcelain tiles are highly resistant to heat due to their dense and non-porous nature. This makes them suitable for areas exposed to high temperatures, such as fireplaces, kitchen countertops, or outdoor spaces. Ceramic tiles, while also heat resistant, are less durable under extreme heat and may crack or lose their glaze over time.
Porcelain’s ability to withstand heat makes it a preferred choice for long-lasting installations in temperature-sensitive environments. To verify this characteristic, consider the intended use and select tiles rated for thermal performance.
Wrap-up
In summary, following the above steps you will be able to easily distinguish between ceramic tiles and porcelain tiles. The right selection can provide the desired results and transform your space into an aesthetic masterpiece.
You May Also Like:



















